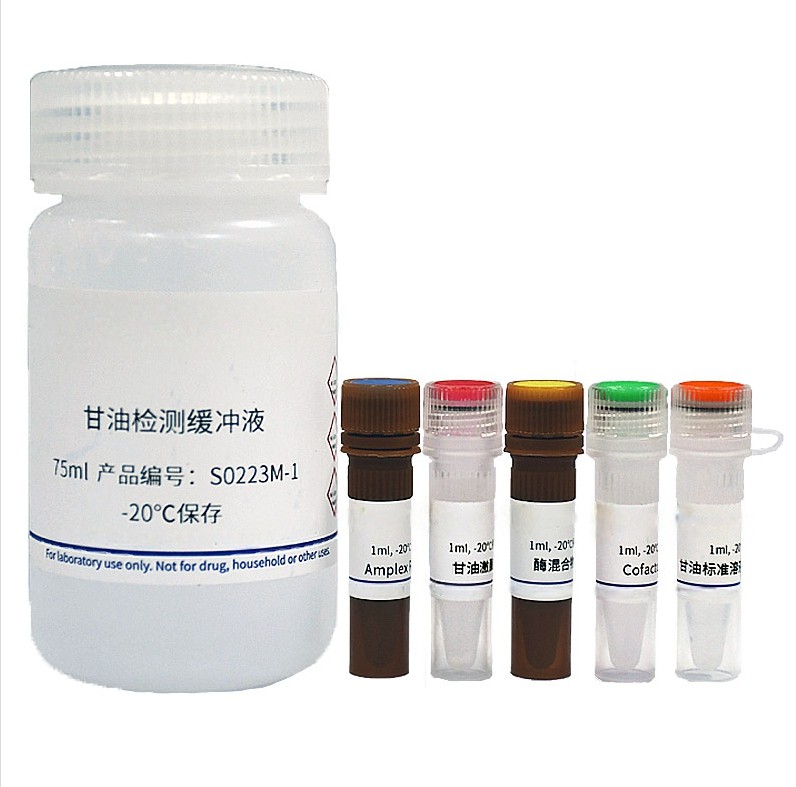
Amplex Red Glycerol Assay Kit S0223
The Amplex Red Glycerol Assay Kit provides a highly sensitive, fluorometric method for detecting free glycerol in biological samples like serum, plasma, and cell culture supernatants.
Koolbio Amplex Red Glycerol Assay Kit provides sensitive, rapid, and simple colorimetric and fluorometric methods for measuring the content of glycerol in serum, plasma, tissue or cell, urine, biological fluids, tissue or cell culture supernatant. This kit only detects free glycerol, not glycerol in triglycerides.
This kit provides high detection sensitivity, wide linear detection range, and requires minimal sample volume. The absorbance and fluorescence intensity of products generated from the assay are positively correlated with the glycerol content within 20-500μM and 2-200μM, respectively. The fluorometric method provided by this kit is much more sensitive, allowing for the use of smaller sample volumes.
This kit offers flexible use, rapid assay, and wide applications. Both fluorometric and colorimetric methods are offered by this kit and the fluorometic method is approximately 10 times more sensitive than the colorimetric method. The entire assay can be completed in approximately 30 minutes. This kit is compatible with serum, plasma, urine, cell culture supernatants, and cell/tissue samples from mice, rats, humans, and other species. It is suitable for both small sample sizes and automated high-throughput screening systems.
This kit is highly specific in detecting free glycerol. The interference from Glycerol-3-phosphate and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in samples can be well eliminated, making the assay results more accurate.
Glycerol is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, clear, viscous liquid. Glycerol has the molecular formula of C3H8O3 and a molecular weight of 92.09. The chemical structure of glycerol is different from that of carbohydrates and they belong to different classes of chemicals. Glycerol does not normally alter blood glucose or insulin levels when absorbed by the body. It is a commonly used sweetener and humectant in the food industry and mostly found in sports foods and milk substitutes. Because glycerol increases the water content of body tissues, it enhances the body's ability to exercise in high temperature environments. Glycerol is widely used in the production of food, beverages, solvents, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, so quantification of glycerol is important in Research and Development [1].
Glycerol is the main component of triglycerides, the most important storage form of fat, and an important metabolite produced during oxidation and energy metabolism. When ingested by the body, most of fat is emulsified into small particles by bile. Lipases secreted in the pancreas and small intestines hydrolyze fat into free fatty acids and glycerol monolipids. Glycerol monolipids and long-chain fatty acids are absorbed and resynthesized into triglycerides in small intestines. Under physiological conditions, triglycerides are hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipolysis to produce glycerol and free fatty acids (FFA) which are released into the bloodstream. The generated glycerol however cannot be reabsorbed and utilized by adipose tissues, so both glycerol and free fatty acid levels in the blood are very effective and important indicators of lipolysis levels, as well as important indicators in the development of many related drugs [2-3].
The Amplex Red is a fluorogenic probe highly sensitive to H2O2. In the presence of horseradish peroxidase (HRP), Amplex Red reacts with H2O2 in a 1:1 ratio, producing highly fluorescent resorufin at Ex/Em=571nm/585nm, with strong absorbance as well at 571nm. Therefore, this kit allows for free glycerol detection using both fluorogenic and colorimetric methods.
Please refer to Figure 1 for the working principle of this kit. In the presence of ATP, glycerol is phosphorylated by glycerol kinase (GK) into glycerol-3-phosphate which is then oxidized by glycerol phosphate oxidase (GPO) to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and H2O2. The content of glycerol can then be quantified by measuring the fluorescence or absorbance of the resorufin produced from the reaction between H2O2 and Amplex Red, as the fluorescence intensity and absorbance value of resorufin are positively correlated to the content of glycerol.

Figure 1. Working principle of koolbio Amplex Red Glycerol Assay Kit (S0223)
This kit provides a glycerol standard solution, which can be used to set up standard curves (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Standard curves prepared using the Amplex Red Glycerol Assay Kit (S0223). When assayed using the colorimetric method (Figure on the left), the A570 is positively correlated with the glycerol content within 20-500μM. However, when assayed using the fluorometric method (Figure on the right), the fluorescence intensity is positively correlated with the triglyceride content within 2-200μM. This figure is for reference only, which may vary depending on different experimental conditions.
According to the instructions of this kit, S0223S and S0223M provide sufficient reagents for 100 and 500 assays, respectively.
Instructions for Use:
1. Sample preparation.
a. Preparation of blood samples: To obtain serum, allow the whole blood to sit at room temperature (around 25℃) for 30 minutes to 2 hours. Do not vigorously shake to avoid hemolysis. After the whole blood has naturally coagulated, centrifuge at approximately 1000-2000×g for 10 minutes at 4℃, and carefully collect the yellow supernatant (serum), without disturbing the white or pale-yellow precipitate. To prepare plasma samples, anticoagulate the whole blood with heparin or EDTA. Centrifuge at approximately 1000-2000×g for 10 minutes at 4℃, and collect the yellow or pale-yellow supernatant (plasma), without disturbing the white precipitate. Both serum and plasma should be kept on ice for immediate use, or aliquoted and stored at -20℃ or -80℃ for future analysis. The frozen serum or plasma samples should be thawed completely and kept on ice before use.
b. Preparation of cell or tissue samples: For adherent cells, wash once with PBS (C0221A) and remove all the liquid. For suspension cells, centrifuge at an appropriate speed (e.g. 100-500×g) for 5 minutes to collect cells in a centrifuge tube, and discard all the supernatant. For adherent cells, pipette appropriately to detach cells from the culture vessel and transfer cells to a centrifuge tube. For tissue samples, add 100-200μl of isopropanol per 10-20mg of tissues. For cultured cells and tissues, control the volume at 100-200μl and homogenize on ice or at 4℃ using the TissueMaster™ High-throughput Tissue Homogenizer with 1.5/2ml × 48 Adaptor) (E6618), TissueMaster™ Handheld Homogenizer (E6600), or a glass homogenizer. Alternatively, increase the volume to 400-500μl and homogenize using a bead homogenizer. Centrifuge at approximately 12,000×g for 3-5 minutes at 4℃ and collect the supernatant for subsequent assay.
Note 1: Samples prepared with isopropanol should be diluted at least 5-fold with the Assay Buffer (i.e. the isopropanol content in samples used for the assay should not exceed 20%).
Note 2: All operations should be performed at 4℃ or on ice. Cell or tissue lysates not to be immediately assayed can be frozen at -20℃ or -80℃.
Note 3: Isopropanol is volatile and evaporates easily. The isopropanol can be replenished to the initial sample volume before assay. When similar degree of evaporation occurs in all samples, it is not necessary to replenish the evaporated isopropanol. However, when calculating the concentration of the sample, the volume of evaporated isopropanol should be considered.
c. Preparation of cell culture supernatant samples: For adherent cells, directly aspirate the culture medium; for suspension cells, take the culture medium after centrifugation.
2. Reagent preparation
a. Thaw the Glycerol Standard (10mM) and Assay Buffer, and equilibrate to room temperature before use. Keep other reagents on ice for use, and store at -20℃ immediately after use.
b. Preparation of Glycerol Assay Working Solution (80µl for each reaction): Mix 72μl Glycerol Assay Buffer, 2μl Amplex Red, 2μl Glycerol Kinase, 2μl Enzyme Mix, 2μl Cofactor to obtain 80μl Glycerol Assay Working Solution. The Working Solution can be used on the same day if stored at 4℃ or on ice protected from light, but it is recommended to use promptly after preparation. Based on the number of test samples (including standards), prepare an appropriate volume of Glycerol Assay Working Solution as follows:.
| Number of Samples | 1 | 10 | 20 | 50 |
| Glycerol Assay Buffer (μl) | 72 | 720 | 1440 | 3600 |
| Amplex Red (μl) | 2 | 20 | 40 | 100 |
| Glycerol Kinase (μl) | 2 | 20 | 40 | 100 |
| Enzyme Mix (μl) | 2 | 20 | 40 | 100 |
| Cofactor (μl) | 2 | 20 | 40 | 100 |
| Working Solution (µl) | 80 | 800 | 1600 | 4000 |
Note: Due to the small amount of Enzyme Mix and its tendency to sediment, centrifuge it briefly and mix well before use.
3. Assay procedure
a. Prepare a glycerol standard curve using colorimetric or fluorometric method (Fluorometric method is recommended for small volume of samples).
(a) Colorimetric method: Take 10μl of Glycerol Standard (10mM), add 190μl of Assay Buffer (For cells or tissue samples prepared with isopropanol, use the Assay Buffer with the same isopropanol content as the sample and the isopropanol content in standard solution should not exceed 20%), and mix well to obtain a 500μM glycerol solution. Add 0, 4, 8, 12, 16 and 20 μl of 500μM glycerol solution into designated wells of 96-well plate, and make up to 20μl with the corresponding buffer. The final concentrations of glycerol standard in corresponding wells are 0, 100, 200, 300, 400 and 500μM, respectively.
Note: Transparent 96-well plates should be used for the colorimetric method.
(b) Fluorescence method: Take 4 μl of glycerol standard solution (10 mM), add 196μl of Assay Buffer (if assaying isopropanol-prepared cell or tissue samples, Assay Buffer with the same content of isopropanol as that of the sample can be used, but the content of isopropanol in the 50μl of the standard should not exceed 20%), and mix well to obtain a glycerol standard solution with a concentration of 200μM. Take 0, 1, 2, 5, 10 and 20μl of 200μM glycerol standard solution and add it into the standard wells of 96-well plate, and make up to 20μl with Assay Buffer or Assay Buffer containing appropriate amount of isopropanol, at this time, the concentration of the standard curve is 0, 10, 20, 50, 100 and 200μM, respectively.
Note: Use a black 96-well plate for fluorescence assay.
b. Add 1-20μl of diluted sample to designated wells of a 96-well plate and make up to 20μl with the buffer used for standard dilution. At the same time, add 20μl of buffer into blank control wells.
Note 1: To ensure the values are within the range of the standard curve, samples can be tested with multiple dilutions to determine an optimal dilution factor for the sample. The total dilution factor of the sample is recorded as n. The dilution factor in step 1b should be counted as well. For example, if the dilution factor in 1b is 5, and 4µl of the sample further diluted by 10-fold in this step is added into the reaction, then the total dilution factor (n)=5×10×20/4=250.
Note 2: When isopropanol-prepared cell or tissue samples are used for the assay, make sure that the isopropanol content in the final reaction system should be no more than 10%.
c. (Optional) Glycerol-3-phosphate or hydrogen peroxide in samples may interfere with the assay of glycerol. In such an event, set up sample background control wells as in step 3b, and add the same volume of Glycerol Assay Working Solution (without Glycerol Kinase) in step 3d.
d. Add 80μl of Glycerol Assay Working Solution to each well, mix well, and incubate at 37℃ for 30 minutes in the dark.
Note 1: If the glycerol content in samples is high, the reaction time can be shortened appropriately (e.g. 15 or 20 minutes). If the fluorescence intensity or absorbance value is too low, the reaction time can be extended accordingly (e.g. 60 minutes or 90 minutes).
e. For colorimetric method, measure the absorbance at 570nm. For fluorometric method, examine the fluorescence at Ex/Em=560nm/590nm.
f. Plot a standard curve and calculate the concentration of glycerol in samples (A). If the sample background signal is relatively high, subtract the background signal from the sample reactions. The concentration of triglycerides in samples can be calculated as follows: C (μM) = A × n, wherein A is the glycerol concentration (μM) determined from the standard curve in step 3f; n is the total dilution factor of the sample calculated from step 3b.
The mass concentration (μg/ml) = C × 0.09209 (The molecular weight of glycerol is 92.09).

 sales
sales